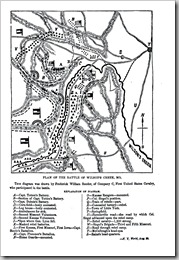
August 10.—Gen Lyon’s column marched until 2 A. M., when it was halted for two hours. Capt. Gilbert’s regulars were thrown out as skirmishers at 4 A. M., and the column moved forward. At 5 o’clock the enemy’s pickets were driven in, and soon after the army came in sight of the rebels’ position. McCulloch’s camp extended in a valley along Wilson’s Creek for three miles, and followed the bends of the streams to the north at its western extremity, and to the south at the eastern. Siegel’s attack was to be made at the latter point, and Lyon moved, therefore, upon the western and northern extremity, down the head of the valley. Blair’s First Missouri Regiment at about 6 o’clock drove a full regiment of infantry from a ridge at the end of the encampment, and at the same time Totten’s battery threw some shells among the enemy’s tents. Blair’s regiment moved forward up a second ridge, upon which they encountered a Louisiana regiment. Here they were reinforced, and finally gained the summit, driving the rebels before them. Two companies of regulars were at this time sent across the creek eastwardly to engage a rebel force in that direction, but were compelled to retire; when Lieut. Dubois opened his battery from the second ridge won, and threw a number of shells which exploded with great effect, and completely routed this body. Blair’s regiment was now withdrawn, and the Iowa First ordered to take its place, and the Kansas regiments to support the Iowa First. An attempt to charge with his cavalry was next made by McCulloch, but the charge was entirely broken by the fire of Totten’s battery. Both batteries were soon in position, and the battle resolved itself into the enemy’s attempt to dislodge them, and regain the ridges from which he had been driven. In this attempt he was repeatedly foiled. At about nine o’clock, as the enemy came on again, Gen. Lyon, who had received three wounds, put himself at the head of the Iowa First to lead a charge with the bayonet, when he received a rifle ball in though breast and fell dead. His fall, however, was not generally known. Major Sturgis assumed the command, and the battle went on.—Mean time, Gen. Siegel made his attack upon McCulloch’s right, drove the rebels for half a mile from their position and took possession of that extremity of their camp; but his advance was broken by the fire of a full regiment that he had permitted to approach in the belief that it was a reinforcement from Gen. Lyon. Unable to rally Salomon’s regiment, he was driven back with the loss of five guns. About noon, the enemy’s tents and his whole baggage train were destroyed by fire, supposed to have been his own act The fight still continued in front, and the last advance of the enemy, made at one P. M., was driven back by the whole national force in the field. Immediately after, Major Sturgis ordered a movement toward Springfield, and the whole force fell back in good order. McCulloch made no pursuit. The national loss was 800 in killed and wounded. Though the rebel loss is not known, it is thought to have been very large, as the national artillery fire was remarkably accurate.—(Doc. 175.)
—The Spanish Minister announced to the Secretary of State at Washington, that the seven American vessels captured by the pirate Sumter and carried into Cienfuegos, had been discharged by order of the Spanish Government.— Washington Republican, August 11.
—To-day Lieutenant Budd, commanding the Reamer Resolute, cleared out one of the rebel depots on the Potomac. It has been known for some time that the Herring Creek on the Maryland side, and Machodock Creek opposite on the Virginia side, were the dcpot for Maryland recruits to the rebel army in Virginia. The Resolute having approached within 300 yards of the shore of the creek, was fired on with musketry. A boat was immediately lowered, and Lieut. Budd with twelve men landed. The rebels fled at their approach and were pursued for a mile, but made their escape. Two muskets and a knapsack which they .threw away in flight were picked up. Upon returning to the house abundant evidence that it had been a rebel rendezvous, and papers containing important information, were found. The buildings were destroyed, and ten contrabands found on the premises were brought away.
After leaving the creek, Lieut. Budd learned from the negroes that there were 800 of the rebels concentrated at the Hague, about five miles back from the river, and that their ferryboat was about three-quarters of a mile up the creek. Meeting the schooner Dana, he took her gun and crew upon the Resolute, and placing the negroes in charge of two men of the Dana, he went up the creek and captured a large boat capable of carrying 25 or 80 men, but saw nothing of the rebels.
—The prize schooner Geo. V. Baker, of Galveston, and her confederate crew of four men in irons, were carried under the guns of Fortress Monroe. The schooner was captured by one of the United States blockading fleet off Galveston, Texas, and sent to New York with the United States crew on board. She was captured yesterday off Cape Hatteras by the rebel privateer York, who put four of her own men on board. Meanwhile the York was seen by the United States gunboat Union, who gave chase and burnt the privateer, but not until the crow had beached her and escaped. The Union then recaptured the Baker, and her crew.
—Isham G. Harris issued an order to the clerks of the county courts of Tennessee, requesting them to search the residences of the people for arms of every description, and to forward such arms to the military authorities at Nashville, Memphis, or Knoxville.—(Doc. 175½.)
—Between the hours of six and seven this evening eighty mounted men, led by Capt. White and a refugee named Talbot, attacked a smaller number of Home Guards at Potosi, Missouri, and were repulsed with a loss of two killed and three wounded. One man of the Home Guards was killed.—St. Louis Democrat, August 12.
—Prof. La Mountain made two successful balloon ascensions at Fortress Monroe, having attained an altitude of three thousand feet. He found the encampment of the Confederate forces to be about three miles beyond Newmarket Bridge, Va. There were no traces of the rebels near Hampton. A considerable force is also encamped on the east side of James River, some eight miles above Newport News. The two cannon mounted at Sewall’s Point toward Old Point, he thinks, are only large fieldpieces. There are, perhaps, one thousand Confederates at Sewall’s Point.—N. Y. Times, August 13.
—The Western Virginia State Convention, in a series of resolutions, declared itself “unalterably opposed to any compromise with the rebels.”—(Doc. 176.)
—The Helena (Arkansas) Shield, of this day, contains the following:—From the Hon. C. W. Adams of this county, who arrived at home a few days since from the northern part of this State, we learn that on last Monday week thirteen hundred Indian warriors—Southern allies —crossed the Arkansas River near Fort Smith, en route for McCulloch’s camp. These Indians are armed with rifle, butcher knife, and tomahawk, and had their faces painted, one half red, and the other black. We also learn that a regiment of mounted Texans likewise crossed the Arkansas at or near Fort Smith, for the same destination.
——-
Late addition to Volume 3:
August 10.—The narrative of Doctor Blaisdell, a physician lately resident in Macon, Ga., was published, in which he pronounced the whole story of Jeff. Davis having taken command in person at Manassas during the fight, a pure fiction.—Cincinnati Gazette.